El Aimani, A., Houari, A., Laasli, SE., Mentag, R., Iraqi, D., Diria, G., Khayi, S., Lahlali, R., Dababat, AA. and [[MOKRINI, F.]] (2022). Antagonistic potential of Moroccan entomopathogenic nematodes against root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne javanica on tomato under greenhouse conditions. [[Scientific Reports 12(1):1-9]]
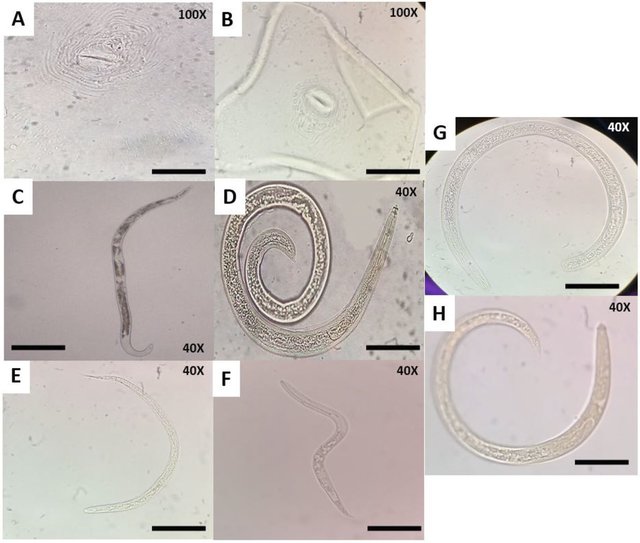
The root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne javanica is a devastating pest affecting tomato production worldwide. Entomopathogenic nematodes (EPNs) are considered very promising biocontrol agents that could be used to effectively manage plant-parasitic nematode. The antagonistic activity of five EPN strains isolated from different fields in Morocco was evaluated against juvenile (J2s) antagonism in soil, the number of